**The world is rapidly transforming, driven by a concept that, while simple in essence, often leaves many scratching their heads: the Internet of Things (IoT). At its core, IoT is about connecting everyday objects to the internet, enabling them to collect and exchange data, ultimately making them "smart." This profound shift, often dubbed the third revolution in information technology, began in the media sector and has since permeated every facet of our lives, from the comfort of our smart homes to the efficiency of industrial automation and the precision of environmental monitoring.** This article delves into the critical components that empower the IoT revolution, specifically focusing on how **IoT SSH Web Free** solutions are shaping its accessibility, security, and affordability. We'll explore the indispensable role of Secure Shell (SSH) for robust device management, the power of intuitive web interfaces for seamless interaction, and the exciting possibilities offered by "free" resources—be it open-source tools or cost-effective cloud services—that democratize IoT development and deployment. Understanding these elements is key to harnessing the full potential of interconnected devices, whether you're an enthusiast, a developer, or a business looking to innovate.
Table of Contents
- Demystifying the Internet of Things (IoT)
- The Indispensable Role of SSH in IoT Security and Management
- The Power of Web Interfaces for IoT Accessibility
- Exploring "Free" Solutions in the IoT Ecosystem
- Synergizing SSH, Web, and Free Tools for Robust IoT Solutions
- Best Practices for Secure and Scalable IoT Deployments
- Challenges and Considerations in the IoT Landscape
- The Future of IoT: Innovation and Integration
Demystifying the Internet of Things (IoT)
The term "Internet of Things" (IoT) often sounds more complex than it is. While a common explanation defines it as "the abbreviation for Internet of Things, translated as the Internet of Things," this can sometimes leave people even more confused. Simply put, IoT is about connecting physical objects to the internet. But what exactly are these "objects"? They can be anything from a smart refrigerator, a wearable fitness tracker, industrial sensors on a factory floor, to intelligent streetlights in a city. These devices are typically embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. IoT is far more than just connecting gadgets; it represents a vast network of interrelated devices that collect and exchange data, often with little to no human intervention. This capability allows organizations to analyze and process data in real-time, leading to informed decisions and significantly enhanced operational efficiency across various sectors. From smart homes that automate lighting and temperature to intelligent cities optimizing traffic flow and waste management, and even smart agriculture monitoring crop health and irrigation, the applications of IoT are incredibly widespread. The advent of inexpensive computer chips and high-bandwidth telecommunications has accelerated this connectivity, resulting in billions of devices now linked to the internet, constantly collecting and exchanging valuable information. This continuous flow of data is what truly powers the IoT ecosystem, enabling unprecedented levels of automation, insight, and control.The Indispensable Role of SSH in IoT Security and Management
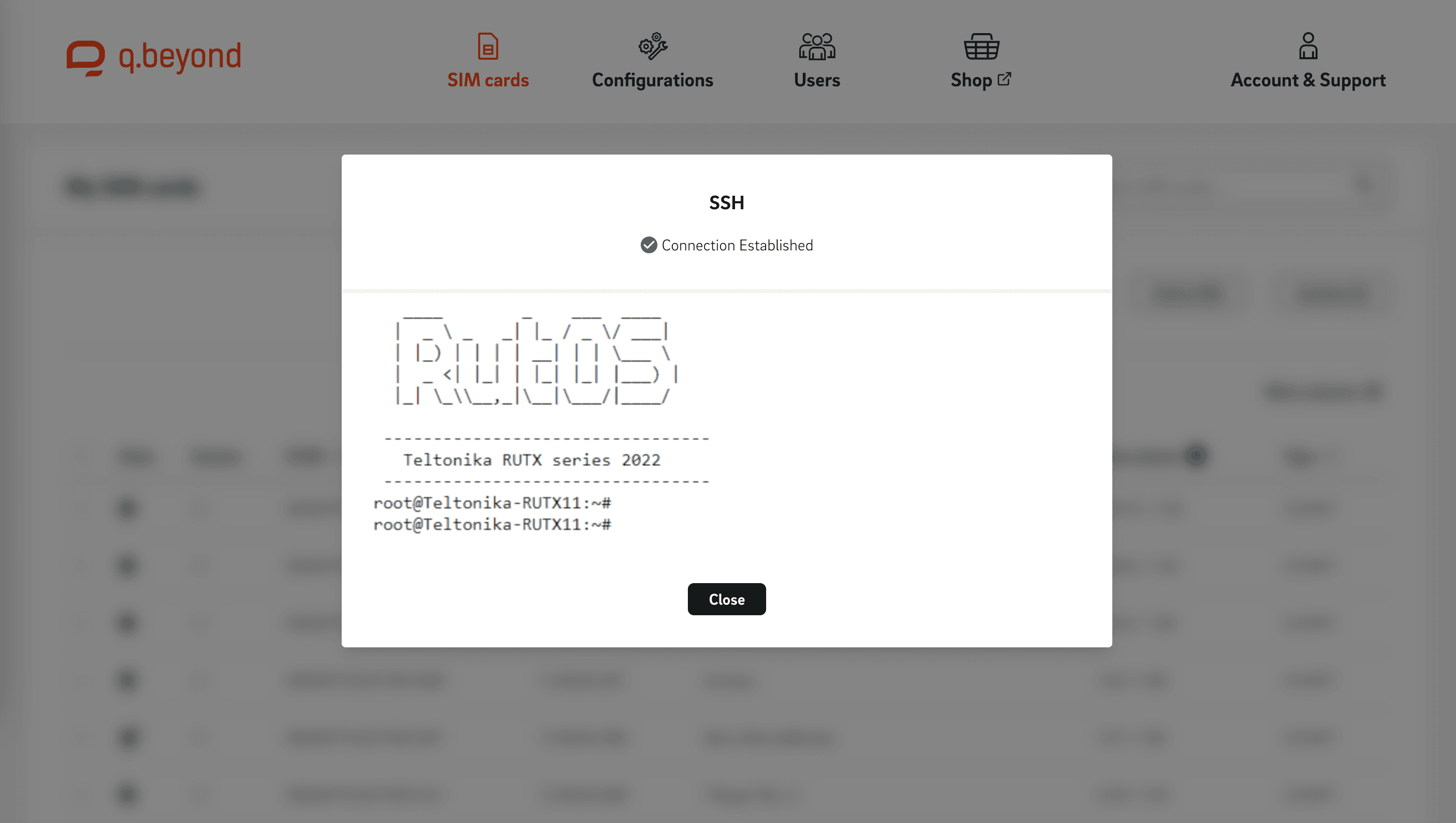
In the realm of IoT, where devices are often deployed remotely and operate autonomously, secure and reliable access is paramount. This is where Secure Shell (SSH) steps in as a cornerstone technology. SSH is a cryptographic network protocol that enables secure data communication between two networked devices. For IoT, it provides a robust and encrypted channel for remote command-line access, file transfers, and even tunneling network services. Without SSH, managing a fleet of IoT devices would be a logistical nightmare and a massive security risk, as any communication would be vulnerable to interception and tampering. It's an essential tool for developers and administrators to maintain control and ensure the integrity of their interconnected systems.Securing Your IoT Devices with SSH
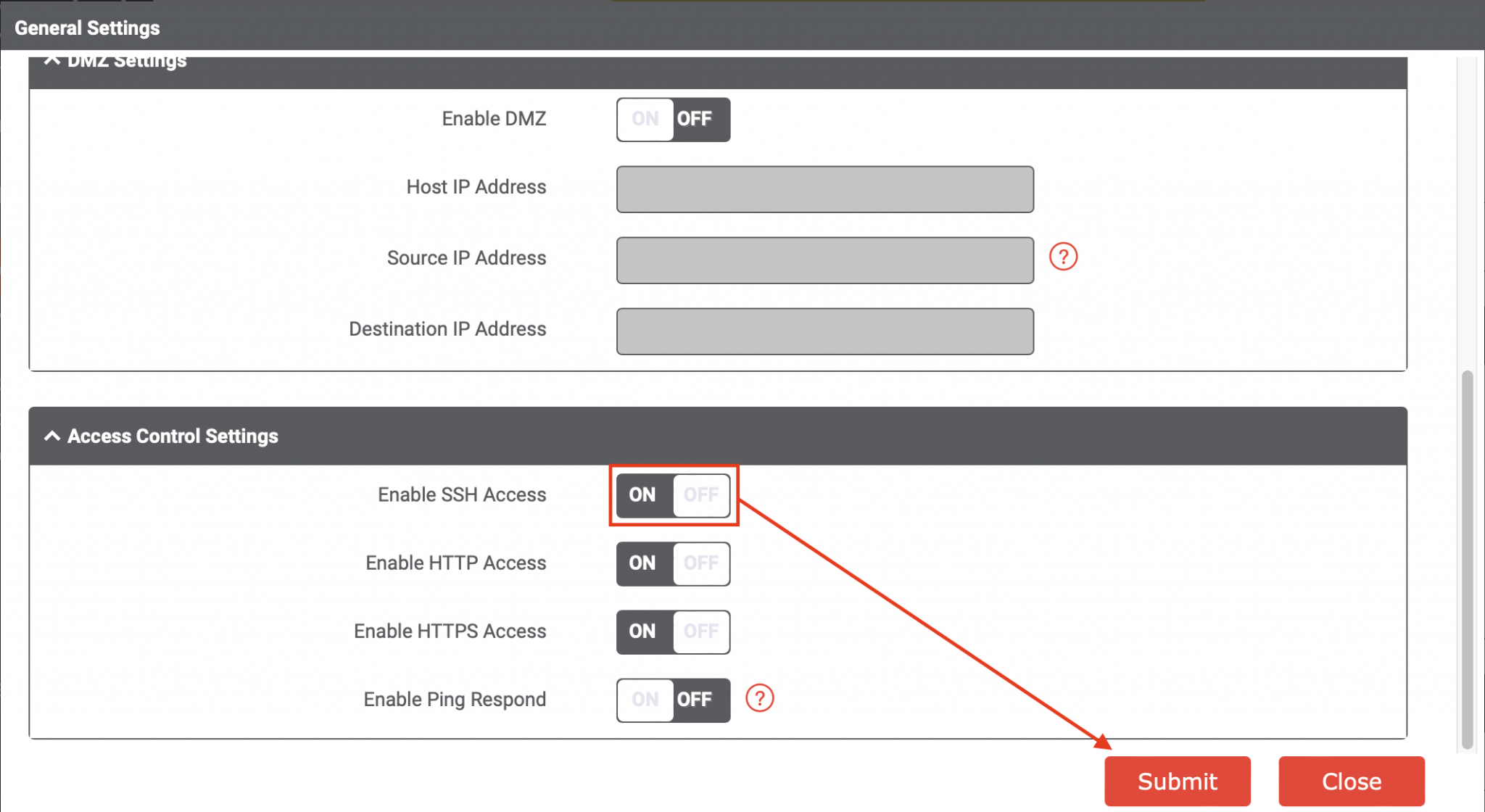
Security is not merely an add-on for IoT; it's a foundational requirement. Given that IoT devices often handle sensitive data or control critical infrastructure, securing them against unauthorized access is non-negotiable. SSH plays a vital role here by providing strong encryption for all data exchanged between the client and the server (your computer and the IoT device). This encryption prevents eavesdropping, ensuring that commands, data, and login credentials remain private. Beyond encryption, SSH offers robust authentication mechanisms. While password-based authentication is common, the industry best practice, especially for IoT deployments, is to use SSH key-pair authentication. This method involves generating a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key that resides on the IoT device and a private key kept securely on your client machine. When you attempt to connect, the device challenges your client to prove it possesses the corresponding private key, without ever transmitting the private key itself. This method is significantly more secure than passwords, which can be brute-forced or guessed. By implementing SSH with key-based authentication, you drastically reduce the attack surface for your IoT devices, protecting them from unauthorized control and data breaches.Remote Management and Troubleshooting via SSH
Imagine having hundreds or thousands of IoT devices scattered across various locations—from a smart farm in a rural area to sensors embedded within a city's infrastructure. Physically accessing each device for maintenance, updates, or troubleshooting would be impractical and costly. This is where SSH truly shines as a remote management tool. With an SSH connection, you can securely access the command line interface of an IoT device from anywhere in the world, as long as it's connected to the internet. This capability allows you to: * **Perform Firmware Updates:** Remotely push and install critical security patches and feature updates, ensuring your devices remain secure and functional. * **Access Log Files:** Retrieve diagnostic logs to understand device behavior, identify errors, and pinpoint the root cause of issues without physical presence. * **Execute System Diagnostics:** Run commands to check system status, resource utilization (CPU, memory), network connectivity, and sensor readings in real-time. * **Configure Settings:** Modify device configurations, adjust operational parameters, or recalibrate sensors remotely. This level of remote control provided by SSH is indispensable for maintaining the health and longevity of IoT deployments, drastically reducing operational costs and improving response times to critical issues. It’s a powerful enabler for truly scalable and resilient **IoT SSH Web Free** solutions.The Power of Web Interfaces for IoT Accessibility
While SSH provides powerful command-line access, it's not always the most user-friendly interface for general users or for visualizing data. This is where web interfaces become invaluable for IoT. A web interface, typically a dashboard or control panel accessible via a web browser, offers an intuitive and graphical way to interact with IoT devices. It abstracts away the complexities of command-line operations, presenting data in an easily digestible format and providing simple controls for device management. This accessibility is crucial for widespread adoption and ease of use, making IoT solutions approachable for a broader audience, not just technical experts.Building User-Friendly IoT Web Dashboards
The effectiveness of an IoT solution often hinges on how easily users can understand and interact with the data and controls it provides. Web dashboards are the primary means of achieving this. They serve as a central hub where data from various sensors can be aggregated, visualized, and analyzed. Think of a smart home dashboard where you can see the temperature in different rooms, control lighting, and monitor security cameras—all from a single, intuitive interface. Building these dashboards can involve various technologies and frameworks: * **Node-RED:** A low-code programming tool for wiring together hardware devices, APIs, and online services. It's excellent for quickly building flow-based applications, including simple web UIs for IoT. * **Grafana:** An open-source analytics and monitoring solution, widely used for creating dynamic and interactive dashboards from various data sources, including IoT sensor data. * **Custom Web Applications:** For more specific needs, developers can build custom web applications using frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js on the frontend, and Node.js, Python (Flask/Django), or PHP on the backend. These applications can connect to IoT platforms or directly to devices (via MQTT, HTTP APIs) to fetch and display data. Key features of effective IoT web dashboards include: * **Real-time Data Visualization:** Charts, graphs, and gauges that update instantly to reflect current sensor readings (e.g., temperature, humidity, energy consumption). * **Interactive Controls:** Buttons, sliders, and toggles to remotely control devices (e.g., turn lights on/off, adjust thermostat settings, open/close blinds). * **Alerts and Notifications:** Visual cues or push notifications when certain thresholds are met or anomalies are detected. * **Historical Data Analysis:** Ability to view past data trends, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions. The combination of robust backend communication (potentially secured by SSH) and a user-friendly web interface creates a powerful and accessible **IoT SSH Web Free** ecosystem, enabling seamless interaction with connected devices.Exploring "Free" Solutions in the IoT Ecosystem
The notion of "free" in technology can be interpreted in several ways within the IoT context. It doesn't necessarily mean zero cost in every aspect, but rather refers to highly cost-effective, open-source, or freely available tiers of services that significantly lower the barrier to entry for IoT development and deployment. This accessibility is a major driving force behind the rapid growth and innovation in the IoT space, allowing individuals, startups, and even large enterprises to experiment, prototype, and deploy solutions without prohibitive upfront investments. The availability of **IoT SSH Web Free** components makes advanced technological solutions attainable for a much wider audience.Leveraging Open-Source Tools for Cost-Effective IoT Development
Open-source software forms the backbone of many "free" IoT solutions. These tools are developed collaboratively and made available with licenses that permit free use, modification, and distribution. This fosters a vibrant community, rapid innovation, and a wealth of resources for developers. Examples of critical open-source tools and platforms for IoT include: * **Operating Systems:** Linux distributions (e.g., Raspbian for Raspberry Pi, OpenWrt for routers) are widely used on IoT devices, providing a stable and flexible foundation. * **MQTT Brokers:** Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is a lightweight messaging protocol ideal for IoT. Open-source MQTT brokers like Mosquitto allow devices to communicate efficiently. * **Web Servers:** Lightweight web servers like Nginx or Apache can be deployed on IoT devices or edge gateways to host web interfaces. * **Development Boards:** While not strictly "software," open-source hardware designs like the ESP32 and ESP8266 microcontrollers offer incredibly low-cost yet powerful platforms for building IoT devices. * **Home Automation Platforms:** Projects like Home Assistant provide a powerful, open-source platform for local control and automation of smart home devices, often integrating with various protocols and services. * **Node-RED:** As mentioned earlier, Node-RED is an open-source visual programming tool that simplifies the development of IoT applications and dashboards. Beyond open-source software, many cloud providers offer "free tiers" for their IoT services. While these tiers have usage limits, they are often generous enough for prototyping, testing, and even small-scale production deployments. Examples include AWS IoT Core, Google Cloud IoT Core, and Azure IoT Hub, all of which provide a certain amount of free messaging, device connections, and data processing each month. This combination of open-source tools and free cloud services significantly reduces the financial burden, making **IoT SSH Web Free** a realistic and powerful approach for innovators worldwide.Synergizing SSH, Web, and Free Tools for Robust IoT Solutions
The true power of **IoT SSH Web Free** emerges when these three components are integrated seamlessly. They are not isolated technologies but rather complementary layers that build a comprehensive and effective IoT ecosystem. Consider a scenario: Imagine you've deployed a network of environmental sensors (e.g., temperature, humidity, air quality) in a remote agricultural field, built using low-cost ESP32 microcontrollers (a "free" hardware platform) running custom firmware. 1. **SSH for Setup and Maintenance:** Initially, you might use SSH to securely connect to each ESP32 (if it has SSH capabilities, or a gateway device it connects to) to configure network settings, update the firmware, or troubleshoot any connectivity issues. This remote access, secured by SSH keys, ensures that even devices in hard-to-reach locations can be managed efficiently. 2. **Web for Monitoring and Control:** The sensor data is then transmitted via MQTT (an open-source protocol) to a central server or a free tier of a cloud IoT platform (e.g., AWS IoT Core). A web application, perhaps built with Node-RED or a custom dashboard, subscribes to this data. Farmers can then access this web interface from their smartphones or computers, viewing real-time graphs of environmental conditions, historical data trends, and even receive alerts if conditions deviate from optimal levels. They might also have web controls to remotely activate irrigation systems or ventilation fans. 3. **"Free" for Cost-Effectiveness:** The entire solution benefits from the "free" aspect: the low-cost ESP32 hardware, open-source firmware, MQTT protocol, open-source web server, and potentially a free tier of a cloud service for data ingestion and processing. This makes the entire solution highly cost-effective, allowing for widespread deployment without significant capital expenditure. This synergy illustrates how SSH provides the secure backbone for device management, web interfaces offer user-friendly access and visualization, and "free" tools and services make the entire solution economically viable and accessible. Together, they create a powerful, scalable, and secure framework for diverse IoT applications.Best Practices for Secure and Scalable IoT Deployments
While the combination of **IoT SSH Web Free** offers immense potential, ensuring the security and scalability of your deployments is paramount. Neglecting these aspects can lead to significant vulnerabilities, data breaches, and operational failures. 1. **Strong Authentication and Authorization:** * **SSH Keys Over Passwords:** Always prioritize SSH key-pair authentication for device access. Disable password-based SSH login where possible. * **Least Privilege Principle:** Grant only the minimum necessary permissions to users and devices. * **Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):** Implement MFA for accessing critical IoT platforms and management interfaces. 2. **Regular Software and Firmware Updates:** * **Patch Management:** Establish a robust process for regularly updating device firmware and software components to patch known vulnerabilities. Many IoT attacks exploit outdated software. * **Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates:** Implement secure OTA update mechanisms to facilitate remote patching of devices. 3. **Network Segmentation:** * **Isolate IoT Devices:** Place IoT devices on a separate network segment (VLAN) from your main corporate or home network. This limits the blast radius if an IoT device is compromised. * **Firewall Rules:** Implement strict firewall rules to control inbound and outbound traffic for IoT devices, allowing only necessary communication. 4. **Data Encryption:** * **Encryption in Transit:** Ensure all data communicated between devices, gateways, and cloud platforms is encrypted using protocols like TLS/SSL (for web and MQTT over TLS). SSH inherently provides this for command-line access. * **Encryption at Rest:** Encrypt sensitive data stored on devices or in cloud databases. 5. **Secure Boot and Hardware Root of Trust:** * For critical applications, use devices that support secure boot, ensuring only trusted firmware can execute. A hardware root of trust provides a secure foundation for cryptographic operations. 6. **Monitoring and Auditing:** * **Log Management:** Collect and analyze logs from IoT devices and platforms to detect suspicious activity. * **Anomaly Detection:** Implement systems to identify unusual patterns in device behavior or data flow that might indicate a compromise. 7. **Physical Security:** * Protect physical access to devices, especially in accessible locations, to prevent tampering or theft. 8. **Vendor Security Assessments:** * When using third-party IoT devices or platforms, thoroughly assess their security practices and certifications. Adhering to these best practices significantly enhances the trustworthiness and reliability of your IoT deployments, protecting both your data and your infrastructure.Challenges and Considerations in the IoT Landscape
While the promise of IoT is vast, its widespread adoption also brings forth a unique set of challenges that need careful consideration. Addressing these issues is crucial for the sustainable growth and responsible implementation of interconnected systems. 1. **Security Vulnerabilities:** Despite the best practices, the sheer volume and diversity of IoT devices create a massive attack surface. Many low-cost devices lack robust security features, making them easy targets for botnets and other malicious activities. The challenge lies in securing every "thing" in the network. 2. **Interoperability:** IoT devices come from countless manufacturers, using various communication protocols, data formats, and operating systems. This fragmentation leads to interoperability issues, making it difficult for devices from different vendors to communicate seamlessly. Standardisation efforts are ongoing but remain a significant hurdle. 3. **Scalability:** Managing billions of interconnected devices and the immense volume of data they generate presents significant scalability challenges for network infrastructure, data storage, and processing capabilities. Solutions must be designed to handle exponential growth. 4. **Data Privacy:** IoT devices collect vast amounts of personal and sensitive data. Ensuring the privacy of this data, complying with regulations like GDPR or CCPA, and building user trust are paramount. Who owns the data? How is it used? These questions are at the forefront of ethical considerations. 5. **Power Management:** Many IoT devices are battery-powered and deployed in remote locations, requiring ultra-low power consumption to ensure long operational lifespans without frequent maintenance. 6. **Connectivity:** Reliable and ubiquitous connectivity remains a challenge, especially in remote areas or environments with signal interference. The reliance on continuous internet access can be a single point of failure. 7. **Ethical Implications:** Beyond privacy, IoT raises broader ethical questions about surveillance, autonomous decision-making, and the potential for job displacement due to automation. Navigating these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach involving technological innovation, industry collaboration, regulatory frameworks, and a strong commitment to user trust and ethical design.The Future of IoT: Innovation and Integration
The journey of IoT is far from over; it's an evolving landscape brimming with potential for further innovation and deeper integration into our lives. The foundational elements of **IoT SSH Web Free** will continue to play a critical role, but new trends and technologies are set to redefine the boundaries of what's possible. 1. **Edge Computing and AI/ML at the Edge:** As the volume of IoT data explodes, processing all of it in the cloud becomes inefficient and costly. Edge computing, where data processing and analysis occur closer to the source (on the device or a local gateway), is gaining prominence. This reduces latency, saves bandwidth, and enhances privacy. Integrating Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning directly on edge devices will enable more intelligent, autonomous decision-making without constant cloud communication. 2. **5G and Faster Connectivity:** The rollout of 5G networks promises ultra-low latency, massive connectivity, and higher bandwidth, which will be transformative for IoT. It will enable real-time applications that require instant responses, support denser deployments of devices, and facilitate new use cases in areas like autonomous vehicles and critical infrastructure. 3. **Enhanced Security Frameworks:** As IoT becomes more pervasive, the focus on robust security will only intensify. Expect to see more sophisticated security protocols, hardware-level security features (e.g., secure enclaves, trusted platform modules), and AI-powered threat detection systems specifically designed for IoT environments. 4. **Digital Twins:** The concept of "digital twins"—virtual replicas of physical objects or systems—is gaining traction. These digital models, fed by real-time IoT data, allow for comprehensive monitoring, simulation, and predictive maintenance, optimizing performance and extending the lifespan of physical assets. 5. **Increased Automation and Intelligence:** Future IoT systems will be even more autonomous, capable of self-healing, self-optimization, and complex decision-making with minimal human intervention. This will drive efficiency across industries, from smart factories to intelligent healthcare systems. 6. **Sustainability and Green IoT:** There's a growing emphasis on making IoT deployments more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. This includes developing low-power devices, optimizing data transmission, and using IoT to monitor and manage environmental resources more effectively. The future of IoT is one of pervasive intelligence, seamless connectivity, and transformative impact. The principles of secure access (SSH), user-friendly interaction (Web), and cost-effectiveness (Free) will remain central, empowering the next wave of innovation that will continue to reshape our world.Conclusion
The Internet of Things is more than just a buzzword; it's a fundamental shift in how we interact with the physical world, driven by the pervasive connectivity of everyday objects. This article has explored the essential pillars that make this revolution accessible, secure, and scalable, particularly focusing on the powerful synergy of **IoT SSH Web Free** solutions. We've seen how SSH provides the indispensable secure backbone for remote management and robust device security, protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access. The power of intuitive web interfaces, on the other hand, democratizes access to IoT data and controls, making complex systems understandable and manageable for a broad audience. Furthermore, the "free" aspect, encompassing open-source tools and cost-effective cloud services, significantly lowers the barrier to entry, fostering innovation and enabling widespread adoption of IoT technologies. As IoT continues to evolve, embracing best practices for security, addressing inherent challenges, and leveraging emerging technologies like edge computing and 5G will be crucial. The future promises even greater intelligence, automation, and integration, transforming industries and improving lives. Whether you're an aspiring developer, a business leader, or simply curious about the connected world, understanding the interplay of SSH, web interfaces, and free resources is key to unlocking the full potential of IoT. What are your thoughts on the future of IoT, especially concerning security and accessibility? Share your insights in the comments below, or explore our other articles to delve deeper into specific IoT technologies and applications!Related Resources:

Detail Author:
- Name : Allene Ziemann
- Username : tremaine89
- Email : julianne71@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1987-10-22
- Address : 671 Monahan Pines East Zula, WA 62033-0311
- Phone : 541-900-4420
- Company : Mohr Group
- Job : Semiconductor Processor
- Bio : Non voluptas aperiam consequatur aperiam. Fugiat at qui et nulla vero iste. Amet dolores facilis tempora sint commodi laudantium.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/osinskib
- username : osinskib
- bio : Libero quasi quibusdam ut.
- followers : 4797
- following : 1828
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/osinskib
- username : osinskib
- bio : Rerum saepe ipsum quasi quo. Voluptas cupiditate deserunt corrupti esse odit.
- followers : 5426
- following : 1129
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@boris_xx
- username : boris_xx
- bio : Ipsum autem aut deserunt iste. Et quibusdam est nam.
- followers : 3871
- following : 516
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/boris831
- username : boris831
- bio : Earum reiciendis architecto et cum similique tenetur officiis. Ipsa omnis reiciendis voluptas ad dolorem qui aliquid. Dolores animi velit illo corporis.
- followers : 4675
- following : 2864